
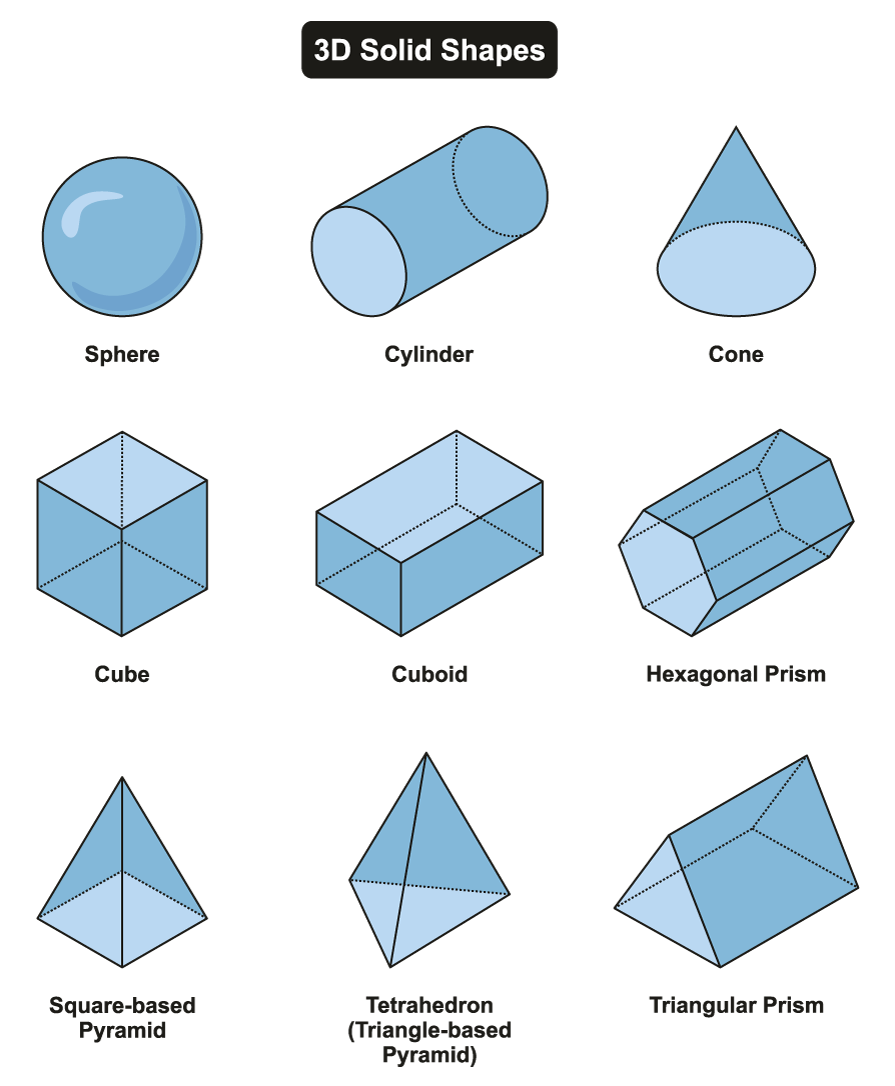
We offer tutoring programs for students in K-12, AP classes, and college. SchoolTutoring Academy is the premier educational services company for K-12 and college students. Cylinder: A three-dimensional object with two circular bases and a.

An example for a regular polyhedron is a cube because it has all congruent faces(squares).Ī convex polyhedron is a polyhedron where the line segment joining any two points on it lies completely in it.Ī concave polyhedron is a polyhedron in which the plane sections are concave.Ī prism is a polyhedron where two of its bases are parallel and the side faces are parallelograms.Ī pyramid is a polyhedron where the base is a polygon and the side faces are triangles with a common vertex. Cube: A three-dimensional object that has six equal-sized square faces and eight vertices. Otherwise it is said to be irregular polyhedron. Note: F+V = E+2 is a formula called Euler’s formula where F,V and E represents the number of faces, vertices and edges respectively.Ī regular polyhedron is a polyhedron whose faces are congruent to each other. For example, the polygonal faces of the cube are the squares.Īn edge of a polyhedron is a line segment where any two of its faces meet. Polygonal faces are the regions by which the polyhedron is bounded. Examples of polyhedrons can be cubes, cuboids, pyramids and prisms etc. We have different three dimensional shapes.Ī polyhedron is a 3D-shape whose faces are polygons where as a non-polyhedron contains no polygon shaped faces. But where as 2d- shapes have only two measurements length and breadth. They look different by observing them from different places and different angles.

Dimension is a property of shapes which tells whether the shape has the height (or depth).Ī three dimensional shape also called as a solid shape is a shape which has 3 measurements length, breadth and height. In mathematics, 3D shapes are nothing but solids that comprises 3 dimensions, namely - length, width, and height.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
